Abstract
Background
Ribonucleotide Reductase (RNR) is responsible for converting ribonucleotides to deoxyribonucleotides required for DNA replication and repair. RNR consists of two subunits, termed subunit 1 (RRM1) and 2 (RRM2). Imbalance in the regulation of RNR activity and control of dNTPs' pool leads to genomic instability and increases mutation rate. RNR expression has been associated with prognosis in pancreatic, non-small-cell lung, breast, and biliary tract cancer. However, RNR expression in chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) and its possible prognostic role have not been investigated yet.
Aim
In this study we evaluate the possible prognostic role of RNR expression in CLL.
Method
The study comprised patients with immunophenotypically confirmed disease at the time of sample collection. Peripheral whole blood samples were collected from 84, 27, 15, and 9 patients before treatment, after one, two, and three lines of treatment respectively.
RNA extraction and reverse transcription were carried out using standard protocols. A Taqman based real-time PCR was performed on a CFX96 RT-PCR system (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). For both the housekeeping and target genes, a Taqman primer/probe mix was used according to the manufacturer's instructions (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA). RRM1 and RRM2 mRNA levels were expressed as an RRM1-2/GAPDH ratio. Western blot analysis was performed to quantify the RRM1 protein levels in a random sample of 41 patients. Antibodies used were: RRM1 #3388, β-actin #4967 and anti-rabbit IgG HRP-conjugated #7074 (Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA). Detection was done using the ECL western blotting reagents.
Statistical analysis was conducted to study the possible correlations between the variables. All reported p values are two-tailed. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05 and analyses were conducted using SPSS statistical software (version 22.0).
Results
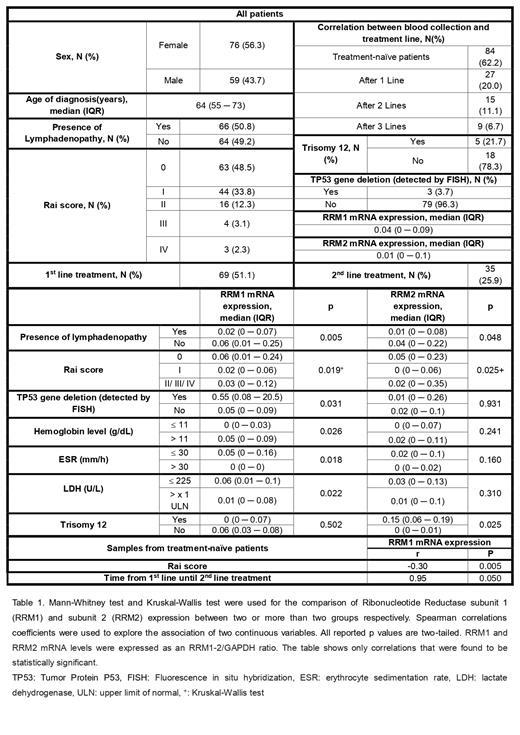
From 135 CLL patients included in the study 56.3% were female and the median age at diagnosis was 64 years. Peripheral blood was collected in 84 treatment-naïve patients (62.2%). Median follow up was 6.66 years (3.47 ─ 11.13) and median time from diagnosis until 1st line treatment was 23.1 months (IQR: 5.8 - 56.5 months). Out of 135 patients, 69 (51,1%) received 1 st line treatment and 35 patients (25,9%) 2 nd line treatment with median time between the two treatment lines being 26.5 months (IQR: 7.8 - 40.8 months). Furthermore, 48.5%, 33.8%, 12.3%, 3.1% and 2.3% of the patients had Rai score 0, I, II, III, IV respectively. The median mRNA expression of RRM1 was 0.04 (IQR: 0 - 0.09) and of RRM2 was 0.01 (IQR: 0 - 0.1).
RRM1 mRNA expression was significantly higher in patients without anemia (p=.025) and without lymphadenopathy (p=.002). Higher values of ESR (r=-.30; p=.028), LDH (r=-.20; p=.026) and Rai score (r=-.18; p=.037) were associated with lower expression of RRM1 mRNA. In addition, TP53 gene deletion detected by FISH was associated with higher RRM1 mRNA expression (p=.036). Significantly higher RRM2 mRNA expression was reported in patients without lymphadenopathy (p=.021) and Rai score 0 (p=.003). Moreover, higher was the expression of RRM2 mRNA in cases with Trisomy 12 (p=.050).
In samples collected before treatment, higher values of RRM1 mRNA expression were statistically significantly associated with lower RAI score (r=-.30; p=.005) and longer time periods between the first two lines of treatment (r=.95; p=.050).
Western blot analysis confirmed detection of RRM1 protein but statistical correlation was not carried out due to lack of material from the whole group of patients.
Conclusion
For the first time, mRNA expression of RRM1 and RRM2 is studied in patients with CLL. These results show RNR involvement in the pathophysiology of CLL. RRM1 and RRM2 mRNA higher expression found in 17p deletion and trisomy 12 cases respectively may be consistent with the existence of a methylation-depended mechanism proposed by other studies. Therefore, these results demonstrate RNR's potential role as a prognostic factor, and make it a probable therapeutic target. A study including a larger number of cases could further confirm our results.
Kyrtsonis: Amgen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Celgene/Genesis Pharma: Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria; Sanofi: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Panagiotidis: Abbvie: Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Janssen: Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Novartis: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Sandoz: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding. Viniou: Sandoz: Research Funding; Takeda: Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Research Funding; Abbvie: Research Funding; Bristol-Myers Squibb: Honoraria, Research Funding; Roche: Research Funding; Astellas: Research Funding; Celgene: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal